Difference between observed and predicted values
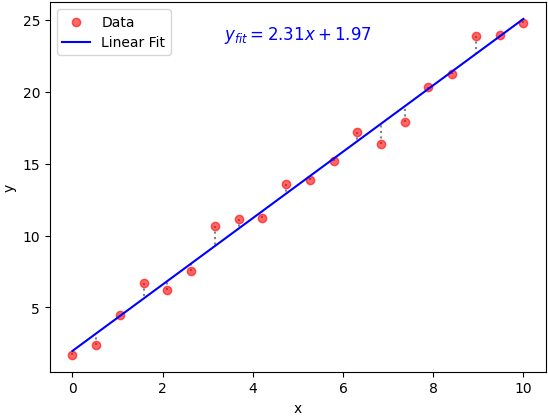
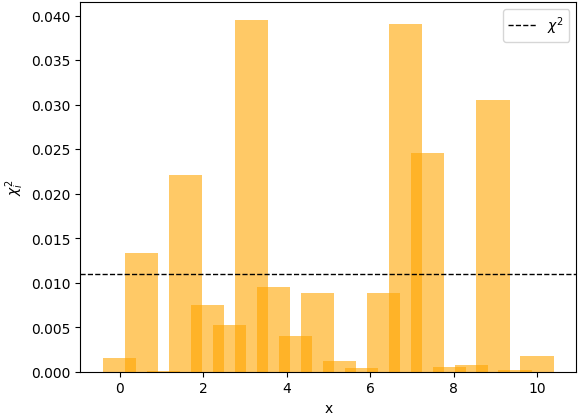
Curve fitting requirements
- Estimate parameter uncertainties
- Support non-linear problem solving
- Easily change optimization algorithm
- Provide high-level tools for setting parameter bounds
Recommended tool (by me)
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Library Name | lmfit |
| Description | High-level interface to non-linear optimization and curve fitting problems |
| GitHub Stars |  1.1k 1.1k |
| Last Commit Date | 13.10.2024 (on 22.10.2024) |
| Built On | SciPy’s curve_fit |
A new non-linear problem
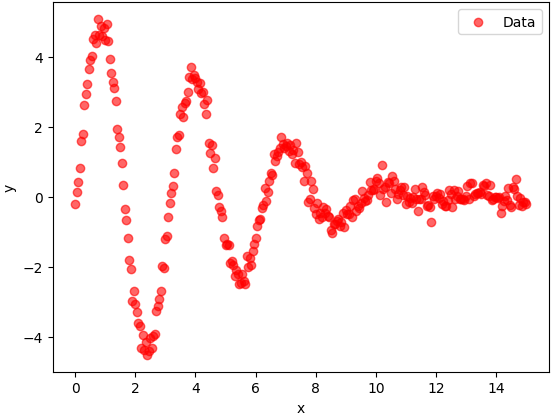 |
 Let's see some code
Let's see some code 
 Let's see some code
Let's see some code 
Problem setup
from lmfit import Minimizer, create_params
def residual(parameters, x, data):
model = (
parameters["amplitude"]
* np.sin(x * parameters["omega"] + parameters["phi"])
* np.exp(-x * x * parameters["gamma"])
)
return model - data
parameters_initial = create_params(
amplitude=10,
gamma=0.1,
omega=3.0,
phi=0.0,
)
minimizer = Minimizer(residual, parameters_initial, fcn_args=(x, data))
result = minimizer.minimize(method="least_squares")
Handling bounds
from lmfit import Parameters
params = Parameters()
params.add('amplitude', value=10, min=0)
params.add('gamma', value=0.1)
params.add('phi', value=0.0, min=-np.pi/2., max=np.pi/2.)
params.add('omega', value=3.0)
from lmfit import create_params
params = create_params(amplitude=dict(value=10, min=0),
gamma=0.1,
omega=3,
phi=dict(value=0, min=-np.pi/2, max=np.pi/2))
Interpret simulation results
[[Fit Statistics]]
# fitting method = least_squares
# function evals = 58
# data points = 301
# variables = 4
chi-square = 12.1867036
reduced chi-square = 0.04103267
Akaike info crit = -957.236198
Bayesian info crit = -942.407756
[[Variables]]
amplitude: 5.03088066 +/- 0.04005821 (0.80%) (init = 10)
gamma: 0.02495457 +/- 4.5396e-04 (1.82%) (init = 0.1)
omega: 2.00026311 +/- 0.00326183 (0.16%) (init = 3)
phi: -0.10264955 +/- 0.01022294 (9.96%) (init = 0)
[[Correlations]] (unreported correlations are < 0.100)
C(omega, phi) = -0.7852
C(amplitude, gamma) = +0.5840
C(amplitude, phi) = -0.1179

 +
+  +
+  =
= 
